Creating a simple write blocker in windows registry.
Overview
In accordance with NIST guidelines, a write blocker serves as a tool enabling users to inspect media while preventing any data writes on the subject media. Its primary function is to preserve data integrity when transferring information from a host machine to an external storage device.
An additional definition of write blocking is the ‘utilisation of a tool that inhibits all computer storage media connected to a computer from being written to or modified’. This concept is especially relevant when discussing hardware write blockers which act as a device positioned between a host machine and an external storage device during data transfer. It ensures that data is transferred in read only mode, preventing any alterations to the data housed on the storage device.
Unfortunately, I don’t have a hardware write blocker.
Thus, the focus here is on software based write blocking, specifically how to activate write blocking within the Windows OS using the registry. The Windows registry, essentially a database storing various options and settings for applications in the operating system, becomes the central point of configuration.
The steps required
The process begins by opening the registry editor through regedit. The focus then shifts to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Control path in the registry editor. Within this hierarchy, a new key named “Storage Device Policies” is created to enable write protection for any external storage device connected to the machine, including USBs, external hard drives or SSDs.
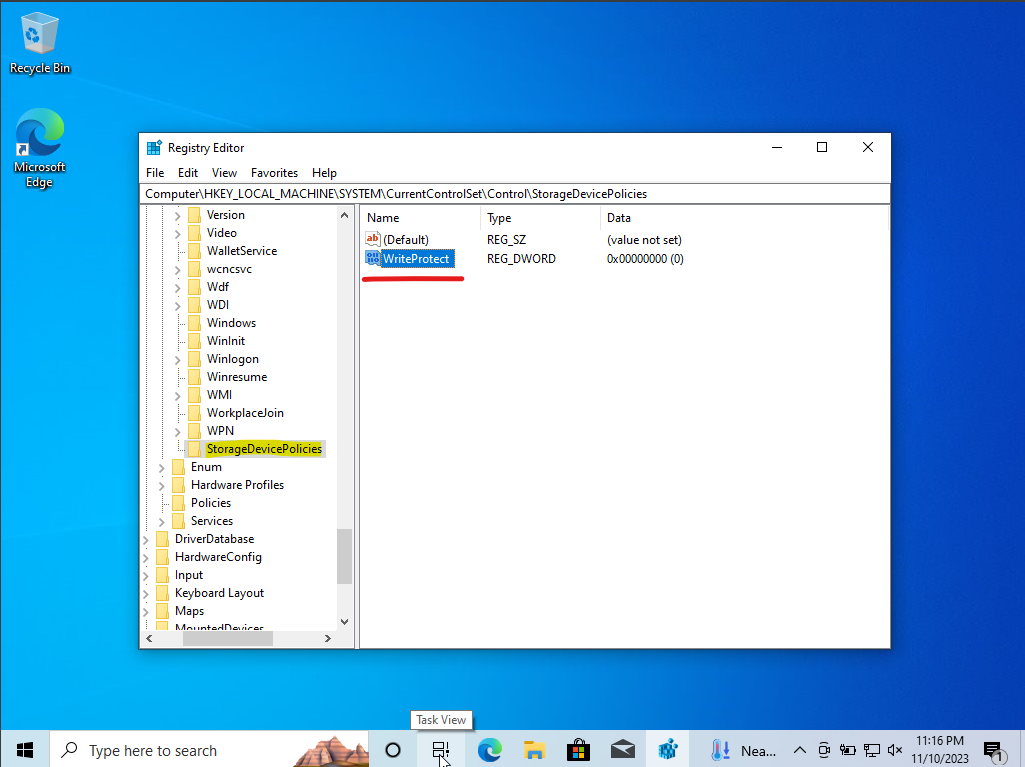
Inside the “Storage Device Policies” key, a new DWORD value called “WriteProtect” is added. The value of “WriteProtect” is set to 0 to indicate write protection is currently off. By modifying the value data to 1, the write protection is turned on.
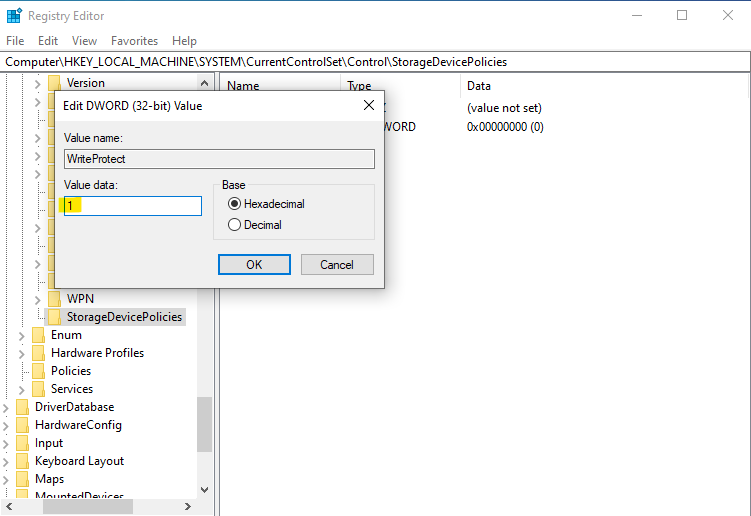
Importantly, devices connected prior to enabling write protection will not be protected. This safeguard is designed to be applicable to any external media attached to the computer after the write protection is activated.
Testing
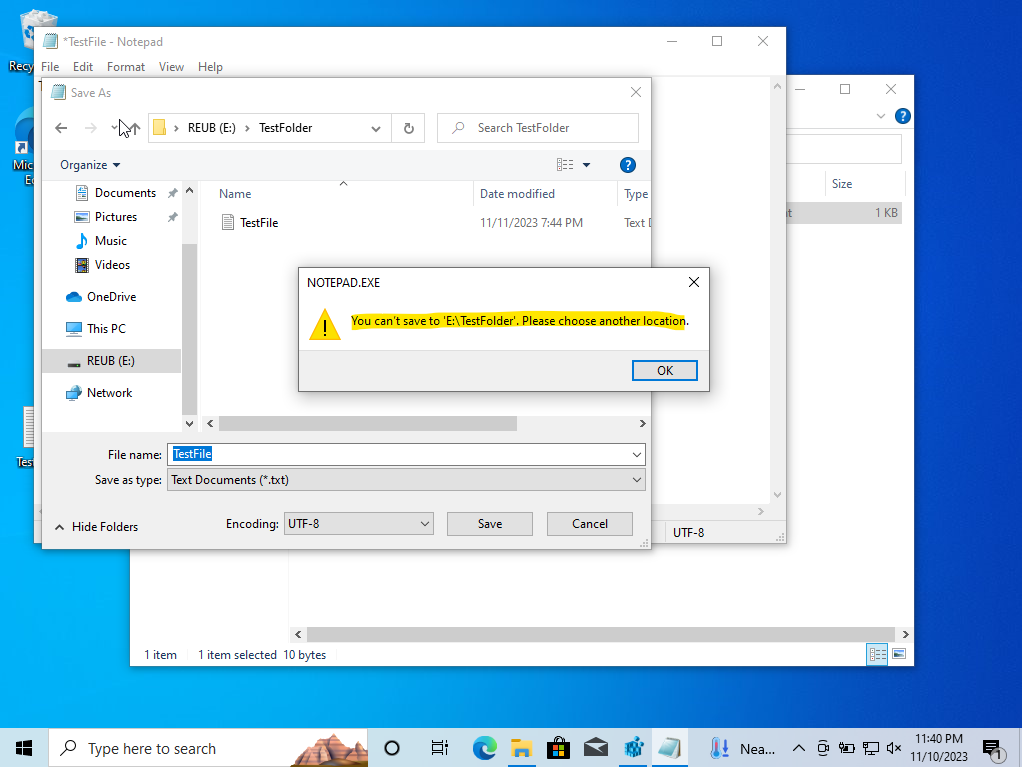
As you can see, attempting to add files from the host machine to the USB results in a write protection error.
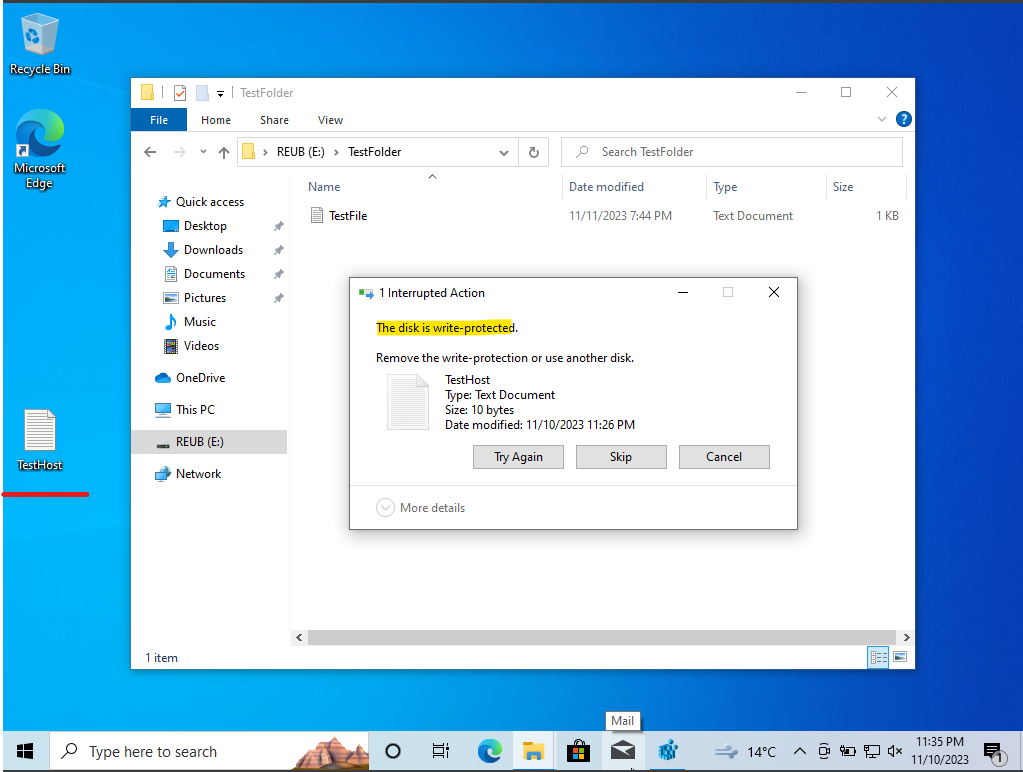
Also, attempts to modify and save existing files on the USB are also restricted due to write protection.